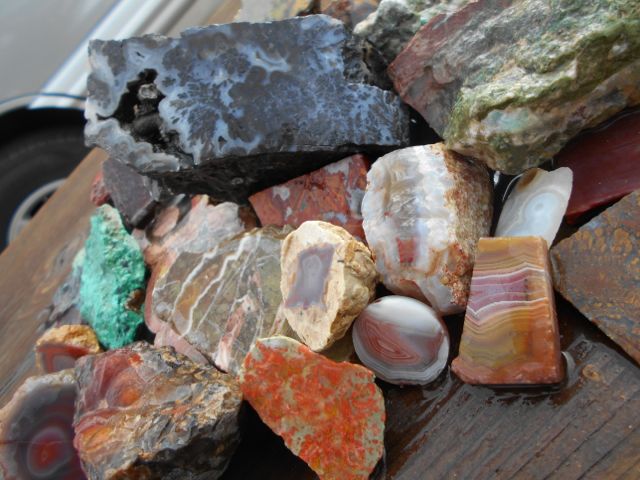


The presence and distribution of layering can help you identify the main type of rock you have.In cross section, layers in a rock will look like different colors stripes on top of one another.You will need to look for these under a magnifying glass. If a rock is layered, it will have different sections that are different colors and may or may not contain small crystals or fossils.The presence and distribution of layering can help you identify the main type of rock you have. Diorite is an example of an intermediate rock.They share minerals with both felsic and mafic rocks and are intermediate in color. Intermediate igneous rocks contain 15-45% mafic mineral crystals.Dunite is an example of an ultramafic rock.These rocks have greater than 85% mafic mineral crystals. Ultramafic igneous rocks are also dark in color and contain higher amounts of the minerals found in mafic rocks.They contain 46-85% mafic mineral crystals and are high in density. Mafic igneous rocks are dark in color and consist mainly of magnesium and iron.

Mafic minerals are olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Felsic rocks have a low density and contain 0-15% mafic crystals.Granite is an example of a felsic rock.Their mineral composition is primarily feldspars and silicates such as quartz. Felsic igneous rocks are light in color.
#Lookthrough rock how to
If you have any questions about how to identify a rock, contact a collector or geologist at a local college or university.Identifying the composition of your rock can be very difficult if you are not an experienced rock collector or geologist.There are four main composition types for igneous rocks: X Research source You will need a rock guide to determine what minerals are present in your rock. Composition refers to the percentage of certain minerals in your rock.
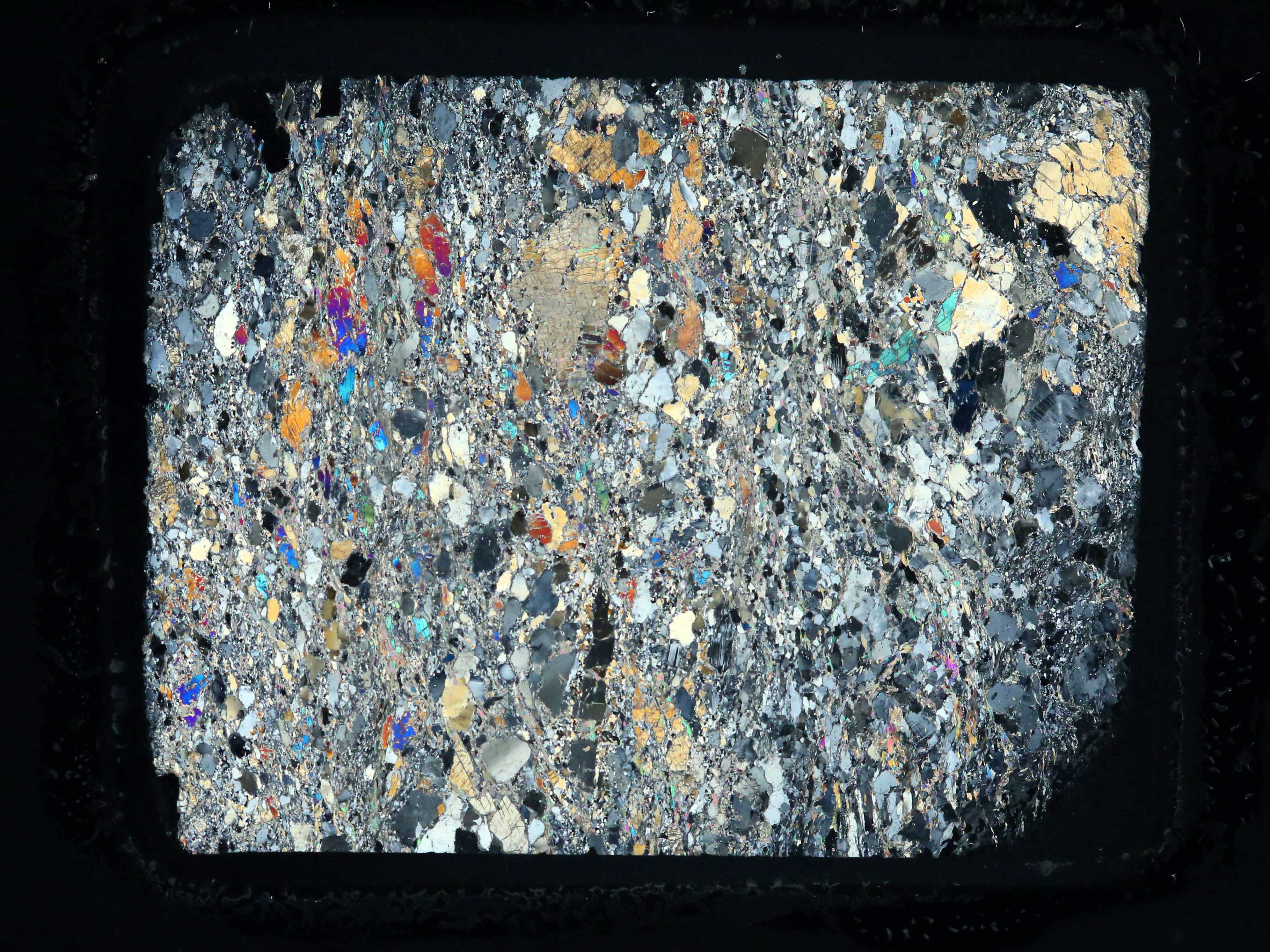 Pyroclastic igneous rock is a texture composed of volcanic fragments ranging from very fine (ash) to very coarse (tuffs and breccias). This also formed with very rapid cooling. Vesicular igneous rocks, such as pumice, look bubbly and form before gases are able to escape as lava forms the rock. Obsidian is the only glassy igneous rock, and can be identified by its dark color. Igneous rocks that form too quickly for crystals to form have what is called a glassy texture. You will need to use a magnifying glass to observe the crystals in aphanitic rocks. Aphanitic igneous rocks have a fine-grained texture and most of their crystals are too small to see with the naked eye.
Pyroclastic igneous rock is a texture composed of volcanic fragments ranging from very fine (ash) to very coarse (tuffs and breccias). This also formed with very rapid cooling. Vesicular igneous rocks, such as pumice, look bubbly and form before gases are able to escape as lava forms the rock. Obsidian is the only glassy igneous rock, and can be identified by its dark color. Igneous rocks that form too quickly for crystals to form have what is called a glassy texture. You will need to use a magnifying glass to observe the crystals in aphanitic rocks. Aphanitic igneous rocks have a fine-grained texture and most of their crystals are too small to see with the naked eye.  Porphyritic igneous rocks have crystals of two different sizes, often with large crystals set in areas of smaller crystals. Phaneritic igneous rocks are composed of interlocking crystals that are smaller than crystals in pegmatitic but still visible with the naked eye. Remember, the slower a rock cools, the larger the crystals will be. These are the slowest cooling type of igneous rocks. Pegmatitic igneous rocks have very large crystals, more than 1 cm in size. There are 7 different texture classes for igneous rocks, each with their own unique features. The most common type of extrusive rock is basalt. government agency responsible for conducting scientific research on the nation's land, natural resources, and natural disasters Go to source You usually can't see these with the naked eye. These are often described as fine-grained rocks. Extrusive rocks have very small, almost microscopic crystals. Extrusive rocks form through very fast cooling of lava above the Earth's surface. When magma is above the earth's crust, it is known as lava. An example of an intrusive rock is granite. Intrusive rocks have larger crystals typically formed together to form the rock mass. government agency responsible for conducting scientific research on the nation's land, natural resources, and natural disasters Go to source Since this occurs below the earth's surface, the magma will cool very slowly. Intrusive rocks form from the cooling of magma deep beneath the earth's surface. The location of the formation of the rock, as well as how fast the magma cools will determine the type of igneous rock. Igneous rocks are formed by cooling magma. Magma is molten rock that flows beneath the earth's surface. Each of these types of rocks will have specific properties that will help you distinguish which type your igneous rock is. Classify igneous rocks into two main types: intrusive or extrusive.
Porphyritic igneous rocks have crystals of two different sizes, often with large crystals set in areas of smaller crystals. Phaneritic igneous rocks are composed of interlocking crystals that are smaller than crystals in pegmatitic but still visible with the naked eye. Remember, the slower a rock cools, the larger the crystals will be. These are the slowest cooling type of igneous rocks. Pegmatitic igneous rocks have very large crystals, more than 1 cm in size. There are 7 different texture classes for igneous rocks, each with their own unique features. The most common type of extrusive rock is basalt. government agency responsible for conducting scientific research on the nation's land, natural resources, and natural disasters Go to source You usually can't see these with the naked eye. These are often described as fine-grained rocks. Extrusive rocks have very small, almost microscopic crystals. Extrusive rocks form through very fast cooling of lava above the Earth's surface. When magma is above the earth's crust, it is known as lava. An example of an intrusive rock is granite. Intrusive rocks have larger crystals typically formed together to form the rock mass. government agency responsible for conducting scientific research on the nation's land, natural resources, and natural disasters Go to source Since this occurs below the earth's surface, the magma will cool very slowly. Intrusive rocks form from the cooling of magma deep beneath the earth's surface. The location of the formation of the rock, as well as how fast the magma cools will determine the type of igneous rock. Igneous rocks are formed by cooling magma. Magma is molten rock that flows beneath the earth's surface. Each of these types of rocks will have specific properties that will help you distinguish which type your igneous rock is. Classify igneous rocks into two main types: intrusive or extrusive.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
